 The sixth question in the quiz for a full-stack developer verifies basic knowledge about Object Relational Mapping in JPA (Java Persistence API).
The sixth question in the quiz for a full-stack developer verifies basic knowledge about Object Relational Mapping in JPA (Java Persistence API).
Correct answer for the fifth question is published.
Two tables have been created in the database: USERS and IMAGES like on the diagram:
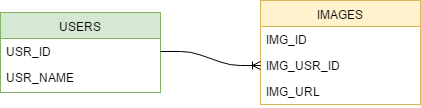
The IMAGE entity is mapped in JPA as follows:
@Entity(name = "IMAGES")
public class Image {
@Id
@Column(name = "IMG_ID")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "IMG_URL")
private String url;
}
The USER entity looks like this:
@Entity(name = "USERS")
public class User {
@Id
@Column(name = "USR_ID")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "USR_NAME")
private String code;
[[missing part]]
private List<Image> images;
}
Which code can be put instead of the [[missing part]] to reflect the database structure? Choose one:
-
@Column(name = "IMG_USR_ID", entity= Image.class)
-
@OneToMany
@JoinTable(
name="IMAGES",
joinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="IMG_USR_ID", referencedColumnName="USR_ID"),
inverseJoinColumns=@JoinColumn(name="USR_ID", referencedColumnName="IMG_USR_ID")) -
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name = "IMG_ID") -
@OneToMany
@JoinColumn(name = "IMG_USR_ID") -
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "IMG_USR_ID")
For the answer scroll down
.
.
.
.
.
.
The correct answer is d. The relation is defined in the USER entity and from that point it is one-to-many relation to IMAGES. The answer b is incorrect because there is no join table - the relation is built on IMG_USR_ID column.
